Marine Heatwaves of 2023 serves as a warning for the future, highlighting the consequences of climate change on our oceans. Rising sea surface temperatures have led to prolonged periods of abnormally warm water known as marine heatwaves.
These events have severe ecological impacts, affecting coral reefs, marine species, and entire food chains. Additionally, they pose challenges for water quality and treatment processes.
This article provides an overview of marine heatwaves, examines the observed data from the 2023 event, discusses future projections, and explores the implications for water quality and treatment.Marine heat waves

Understanding Marine Heatwaves
Marine heatwaves (MHWs) are characterized by extended periods of unusually high water temperatures in the ocean. As Earth’s great heat reservoir, the oceans have absorbed over 90% of the excess heat resulting from greenhouse gas emissions.
While this has slowed atmospheric warming, it has intensified MHWs, leading to significantecological disruptions and consequences.
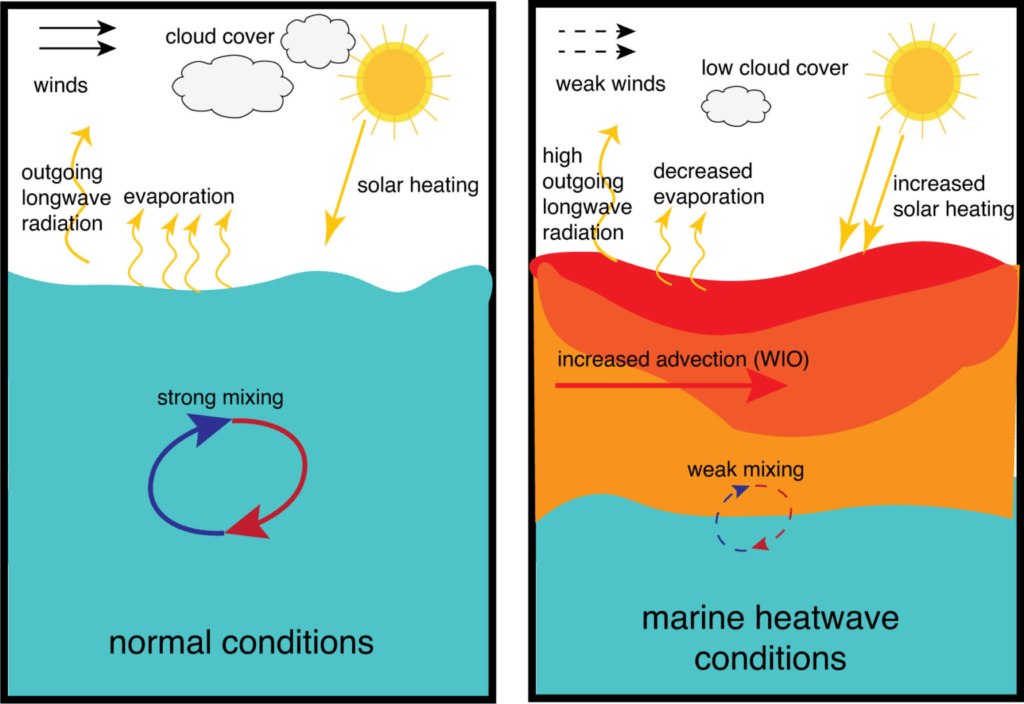
In June 2023, a category 4 heatwave occurred in the north Atlantic off the coast of Ireland, reaching “beyond extreme” conditions in some areas. The elevated sea-surface temperatures were linked to extreme precipitation, thunderstorms, and above-average temperatures across Ireland.
These events were attributed to a combination of natural variability and background warming due to climate change.
Implications for Water Quality caused from Marine heat waves
Marine heatwaves have adverse effects on water quality, posing challenges for various aspects of water management and treatment. The consequences include:
- Harmful Algal Blooms: Warmer waters during heatwaves can trigger the proliferation of harmful algal blooms. These blooms produce toxins that pose risks to human health and can contaminate drinking water sources.
- Reduced Oxygen Levels: Elevated water temperatures and disrupted marine ecosystems during heatwaves can lead to reduced oxygen levels in the water. This reduction in dissolved oxygen can harm aquatic life and impact water quality.
- Increased Turbidity: Heatwaves can cause disturbances in marine ecosystems, resulting in increased turbidity or cloudiness of the water. Higher turbidity levels can hinder water treatment processes and reduce the effectiveness of filtration systems.

Challenges for Water Treatment Processes caused by Marine heat waves
Marine heatwaves present challenges for water treatment processes, especially in coastal areas. The impacts include:
- Algal Bloom Management: Water treatment facilities need to adapt their processes to handle the increased occurrence of harmful algal blooms during heatwaves. Advanced treatment methods and monitoring systems may be required to effectively remove toxins and ensure safe drinking water.
- Enhanced Filtration: The elevated turbidity caused by disrupted marine ecosystems during heatwaves requires enhanced filtration systems in water treatment plants. Upgraded filtration technologies can help maintain the quality and safety of the treated water.
- Energy Demands: Higher water temperatures during marine heatwaves may affect the energy efficiency of water treatment processes. Cooling requirements for equipment and increased energy demands for maintaining optimal treatment conditions may pose additional challenges.
The Importance of Investing in Better Filtration Methods for Water Quality
Climate change and its associated impacts, including more frequent and intense events like marine heatwaves, pose a significant challenge to water quality. These events can lead to increased water contamination, such as harmful algal blooms and elevated turbidity. To effectively remove contaminants and maintain water quality during these extreme events, improved filtration methods are crucial.
Growing Water Demand
With the global population steadily increasing, the demand for water is on the rise, particularly for drinking water supply. However, water sources are facing pollution and strain, making it essential to invest in advanced filtration methods. These methods ensure the availability of safe and clean drinking water, even in the face of growing water demand.
Emerging Contaminants
The presence of emerging contaminants in water sources, including pharmaceuticals, microplastics, and chemicals, is a growing concern for public health. To protect against these contaminants and maintain water safety, better filtration technologies are needed. These advanced methods can effectively remove emerging contaminants and safeguard public health.
Aging Infrastructure
Many water treatment facilities worldwide have aging infrastructure that may not meet the demands of today’s water quality standards. To address this challenge, investing in better filtration methods is crucial. Upgrading filtration technologies allows for the modernization of water treatment facilities, leading to improved treatment efficiency and the ability to meet current water quality requirements.

Zeolite-Based Filter Media for Pretreatment with Marine heat waves
Zeolite-based filter media, particularly Zeomedia, is an invaluable asset as a pretreatment filter in water treatment processes. Its numerous benefits make it a compelling choice. Here’s why:
- Enhanced Filtration Efficiency: Zeomedia possesses a unique porous structure that enables the efficient removal of suspended solids, turbidity, and specific contaminants. By acting as a physical barrier, it effectively captures and eliminates particles, enhancing overall filtration performance.
- Ion Exchange Properties: Zeolites exhibit remarkable ion exchange capabilities, allowing them to remove heavy metals and other ions from water. This characteristic significantly improves water quality and reduces potential health risks associated with these contaminants, ensuring safer drinking water.
- Versatile Application: We can ensure that our filter media finds extensive application across various water treatment processes, including drinking water treatment, wastewater treatment, and industrial water treatment. Its versatility and compatibility with different treatment systems make it an ideal choice for pretreatment filtration in diverse settings.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Zeomedia offers cost advantages due to its extended service life and lower maintenance requirements when compared to traditional filter media. Furthermore, its regenerability and reusability capabilities contribute to long-term operational cost reductions.
- Sustainable Solution: Out filter media stands as a natural and environmentally friendly filter media. Its utilization promotes sustainability by minimizing waste generation and reducing reliance on synthetic filter materials, making it a greener option for water treatment processes.
By incorporating zeolite-based filter media like Zeomedia as a pretreatment step in water treatment processes, overall filtration efficiency can be significantly improved, resulting in enhanced water quality. Furthermore, its sustainable characteristics contribute to responsible water management and conservation efforts.
References:
- Hammainen, H., et al. (2015). Zeolite filtration in drinking water treatment – a review. Water Research, 77, 1-14.
- Zhang, Z., et al. (2021). Zeolite as a versatile functional material for water and wastewater treatment: A comprehensive review. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 104, 1-17.