In the arid landscapes of Saudi Arabia, the pursuit of clean and accessible water has led to a remarkable transformation through water desalination. This article delves into the technical aspects of water desalination in the Kingdom, exploring its historical roots, advancements in technology, and the future challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. The Evolution and Future of Water Desalination in Saudi Arabia
History of water desalination in Saudi Arabia
In the early 1900s, Jeddah took the pioneering step of installing privately-owned distillation condensers to meet the escalating water demand. Subsequently, Yanbu and Jazan followed suit, developing their own seawater distillation condensers.
The nationalization of the industry in 1965 under the Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture marked a turning point, establishing water desalination as a regulated sector. (Read the more about the Historical Foundations and Technological Breakthroughs)

Technological advancements have been instrumental in expanding the desalination capacity. Thermal distillation, utilizing heat to vaporize seawater and separate salt from water, emerged as an early method. In recent years, reverse osmosis, where seawater is forced through a semipermeable membrane to remove salt, has gained popularity due to its energy efficiency.
¿How the desalination process works?
The desalination process involves removing salt and other impurities from seawater or brackish water to make it suitable for drinking or industrial use. The most common methods used in desalination are thermal distillation and reverse osmosis.
Thermal Distillation:
- Seawater is heated to create steam
- The steam is then condensed to separate it from the salt and impurities, leaving behind freshwater.
- This freshwater is collected and treated for us
Reverse Osmosis:
- Seawater is pressurized and passed through a semipermeable membrane.
- The membrane allows water molecules to pass through while blocking salts and other contaminants.
- The resulting freshwater is collected, and the concentrated brine, containing the removed salts, is disposed of.
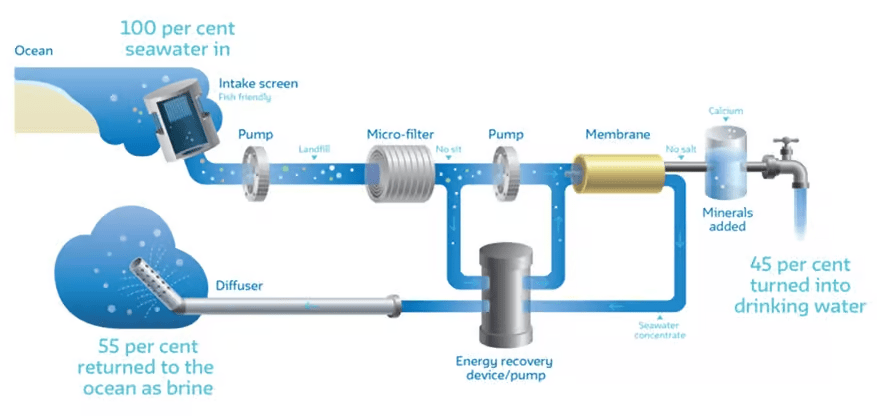
Both methods require energy input, with thermal distillation relying on heat and reverse osmosis needing pressure to push water through the membrane. Advanced technologies and system optimizations have made these processes more efficient over time.
It’s important to note that desalination is a complex process that involves pre-treatment steps to remove larger particles and impurities before the main desalination process. Additionally, post-treatment may be necessary to adjust the water’s pH levels and add minerals to ensure its quality and taste.
Expansion of Desalination Capacity and Energy Generation in the Water Desalination, Saudi Arabia
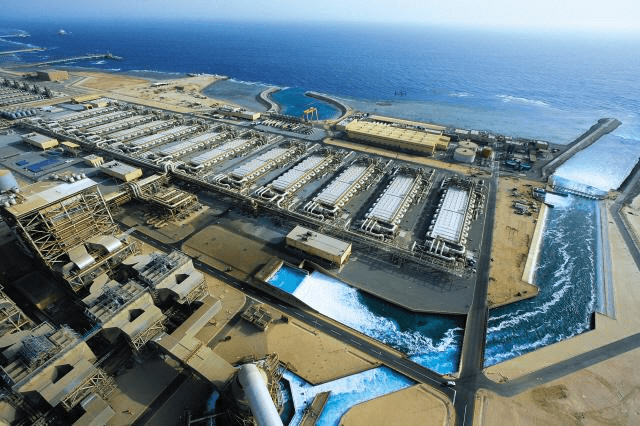
Saudi Arabia has witnessed a significant expansion of desalination plants. Notable examples include the Jubail 2 plant, which saw its annual production capacity increase by 30% from 2014 to 2021, reaching 380 million cubic meters. This growth has enabled the Kingdom to meet the soaring domestic water demand.

Water desalination also contributes to the energy sector. In the process of distillation, a byproduct of water production is the generation of approximately 47 million megawatts per hour of electricity. This dual benefit further strengthens the position of desalination in Saudi Arabia’s sustainable development.
Addressing Challenges and Embracing Renewables
With a growing population and limited water resources, Saudi Arabia faces challenges in ensuring a sustainable water supply. To meet these demands, the government has turned its attention to renewable solutions. The Saline Water Conversion Corp. (SWCC) has actively participated in renewable energy projects aligned with the Vision 2030 blueprint.
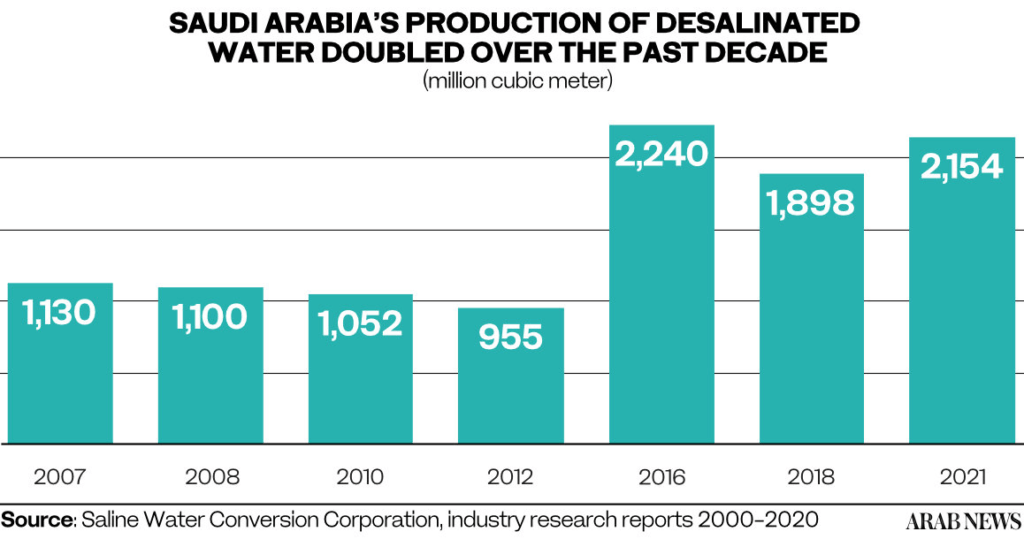
These endeavors aim to reduce the conversion cost of desalination while improving its efficiency and curbing carbon emissions. By integrating renewable energy sources into desalination plants, Saudi Arabia strives to create a more sustainable and eco-friendly water supply.
Choosing the right pretreatment for the future of Water Desalination in Saudi Arabia
Water pretreatment in the desalination process is crucial to remove larger particles, suspended solids, and other impurities before subjecting the water to the main desalination method. While sand filters have been traditionally used in pretreatment, zeolite filter media can offer several advantages in terms of effectiveness and efficiency. The Evolution and Future of Water Desalination in Saudi Arabia
Here’s how zeolite filter media can enhance the water pretreatment process compared to sand:
- Filtration Efficiency: Zeolite has a higher filtration efficiency compared to sand due to its smaller particle size and uniformity. This allows for better removal of suspended solids and smaller particles, resulting in cleaner water.
- Ion Exchange Capacity: Zeolite’s ion exchange properties make it highly effective in removing heavy metals, ammonia, and other contaminants present in the water. It can selectively capture these ions and exchange them with less harmful ones, thereby improving water quality.
- Longer Filter Run Times: Zeolite filter media tends to have longer filter run times compared to sand filters. This means that the zeolite filters require less frequent backwashing or regeneration, reducing water and energy consumption during the pretreatment process.
- Reduced Pressure Drop: Zeolite’s smaller particle size and uniformity contribute to a lower pressure drop across the filter media. This helps maintain a consistent flow rate, reducing the energy requirements of the pretreatment system.
- Compact Design: Zeolite filters can achieve the same or higher levels of pretreatment efficiency as sand filters while requiring a smaller footprint. This compact design is especially beneficial in situations where space is limited.
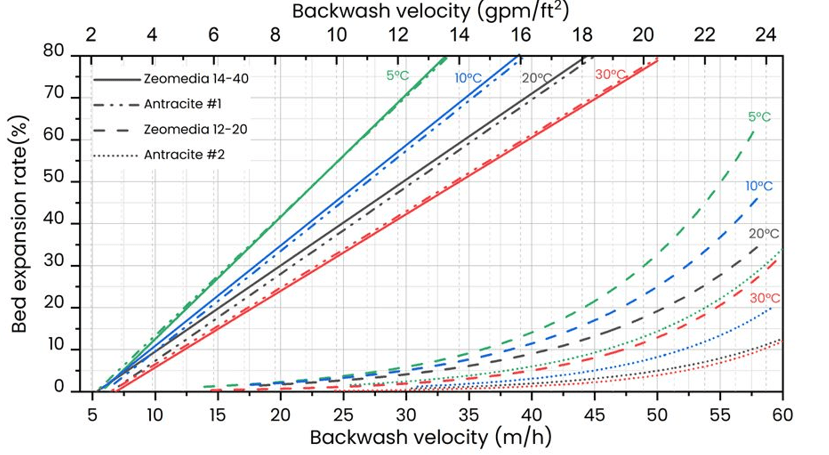
It’s worth noting that the specific design and configuration of the pretreatment system, including the type and size of zeolite media, will depend on the water source, quality, and the desalination process employed. The Evolution and Future of Water Desalination in Saudi Arabia
Future Prospects and Considerations in Water Desalination Process in Saudi Arabia
Projections indicate that Saudi Arabia may require a desalinated water capacity of up to 4.5 billion cubic meters per year by 2040, double the current production levels. Achieving this ambitious target will demand continued innovation, research, and investment in desalination technologies.
In addition to technical advancements, demand management strategies will play a crucial role in balancing water consumption. Awareness campaigns and potential taxation on high water usage are among the methods that may be employed to reduce water demand.
Sources:
- Ghaffour, N., Missimer, T. M., & Amy, G. L. (2013). Technical review and evaluation of the economics of water desalination: Current and future challenges for better water supply sustainability. Desalination, 309, 197-207.
- Elimelech, M., Phillip, W. A., Gadgil, A., & DiGiano, F. A. (2011). Handbook of desalination. CRC Press.
- Al-Ansari, N., Ewais, M., & Javadi, A. A. (2018). Desalination technologies for water treatment and reuse. Journal of Earth Sciences and Geotechnical Engineering, 8(2), 59-72.