When it comes to wastewater treatment, various techniques and chemicals play a vital role in ensuring the efficient removal of contaminants. One such essential chemical is flocculants. In this article, we will delve into the world of flocculants, exploring their purpose, working mechanism, and the benefits they bring to wastewater treatment processes.The importance of floculants in water treatment
We are going to talk about
- Flocculants in wastewater treatment
- Role of flocculants
- Wastewater treatment chemicals
- Flocculation process
- Benefits of flocculants
Introduction toFlocculants: The importance of floculants in water treatment
Flocculants are essential in wastewater treatment, aiding in the aggregation and settling of particles for improved water quality and solid-liquid separation. They bring suspended particles together, forming larger clusters called flocs, making them easier to remove.
Flocculants not only enhance water quality but also remove contaminants and contribute to meeting water quality standards. Various types of flocculants, including inorganic, organic, synthetic, and natural options, offer different characteristics and applications.
Leveraging these flocculants optimizes wastewater treatment processes, leading to cleaner water and a reduced environmental impact. In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into flocculation mechanisms, discuss their significance, explore different types, and examine selection factors for specific applications.
Flocculation Process
Flocculation is a key process in wastewater treatment that involves the aggregation and binding together of suspended particles to form larger clusters called flocs. This process is facilitated by the action of flocculants, which can operate through bridging or adsorption mechanisms.
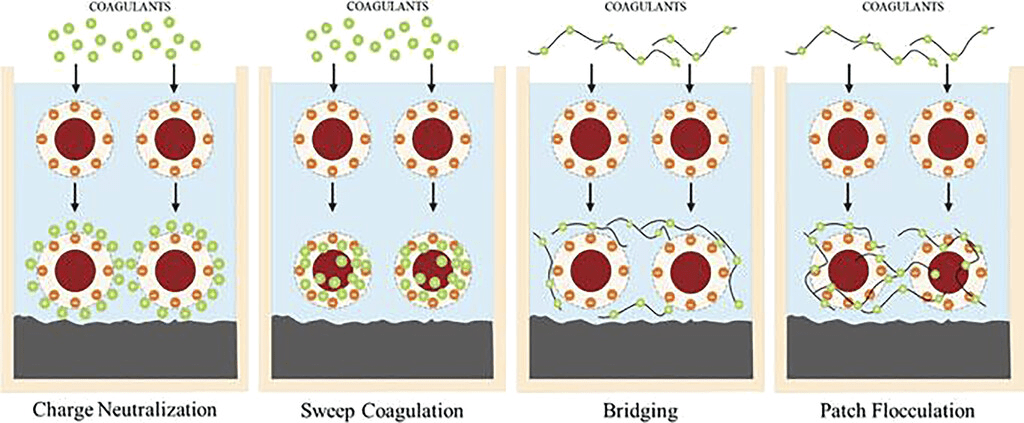
1. Bridging Mechanism:
In the bridging mechanism, flocculants act as bridges between the suspended particles. Flocculant molecules are typically long-chain polymers with numerous functional groups. These functional groups possess a strong affinity for both the suspended particles and the surrounding water molecules. When introduced into the wastewater, the flocculant molecules adsorb onto the surface of the particles, extending their chains into the water.(The importance of floculants in water treatment)
As the flocculant molecules adsorb onto multiple particles, they create bridges or connections between them. This bridging effect brings the particles into closer proximity, allowing for the formation of flocs. The size of the flocs increases as more particles are bridged together, ultimately resulting in larger and heavier aggregates.
2. Adsorption Mechanism:
The adsorption mechanism involves the direct attachment of flocculant molecules onto the surface of the suspended particles. Flocculants can possess a charge opposite to that of the particles, leading to electrostatic attraction between them. Alternatively, they may exhibit a charge similar to that of the particles, resulting in Van der Waals forces or hydrophobic interactions.
When the flocculant molecules adsorb onto the particle surfaces, they create a net positive or negative charge on the flocs. This charge destabilizes the repulsive forces between the particles, allowing them to come closer together and form larger flocs. The adsorption mechanism is particularly effective when dealing with finely dispersed particles that are difficult to settle through gravitational forces alone.
The importance of floculants in water treatment
3. Settling of Suspended Solids:
The flocs formed during flocculation greatly aid in the settling of suspended solids in wastewater. The increased size and weight of the flocs make them more susceptible to gravitational forces, enabling them to settle more rapidly. As the flocs settle, they carry the adsorbed or trapped particles along with them, effectively removing contaminants from the water.
Once settled, the flocs can be separated from the clarified water through processes such as sedimentation or filtration. The choice of separation method depends on the specific requirements of the wastewater treatment process.
The flocculation process not only enhances the removal of suspended solids but also contributes to the overall efficiency of downstream treatment processes. By transforming the dispersed particles into larger, settleable flocs, flocculants assist in reducing the load on subsequent treatment units, such as clarifiers, filters, or centrifuges. The importance of floculants in water treatmen
Understanding the mechanisms of flocculation and the role of flocs in settling suspended solids is crucial for optimizing wastewater treatment processes and achieving the desired water quality standards. By selecting appropriate flocculants and optimizing process parameters, wastewater treatment plants can improve their overall efficiency and minimize the environmental impact of discharged effluent.
Importance of Flocculants in Wastewater Treatment
Flocculants play a vital role in wastewater treatment processes, offering numerous benefits that contribute to efficient and effective treatment. Let’s explore some key advantages of using flocculants:

1. Adsorption Mechanism:
Flocculants greatly enhance the solid-liquid separation process in wastewater treatment. By facilitating the formation of larger and heavier flocs, flocculants increase the settling velocity of suspended particles. This leads to improved sedimentation and clarification, allowing for easier separation of solids from the wastewater.
Enhanced solid-liquid separation reduces the load on subsequent treatment units, such as filters or centrifuges, improving overall process efficiency.
2. Removal of Suspended Particles
One of the primary objectives of wastewater treatment is the removal of suspended particles. Flocculants aid in this removal by agglomerating and aggregating these particles into flocs. The flocs formed are larger and settle more readily, resulting in effective removal of contaminants such as organic matter, inorganic compounds, and pathogens.
The use of flocculants ensures cleaner water by reducing the concentration of suspended solids, thereby improving water quality and meeting regulatory standards.
3. Reduction of Organic Content:
Flocculants can also help in reducing the organic content of wastewater. Organic matter, including proteins, oils, and other carbon-based substances, can be challenging to remove using conventional treatment methods alone. Flocculants, particularly organic and synthetic polymers, have a high affinity for organic molecules.
By binding to these organic compounds, flocculants aid in their removal, leading to a reduction in the organic load of the wastewater. This is particularly important for wastewater discharges into sensitive ecosystems, as it helps prevent oxygen depletion and the associated negative environmental impacts.
4. Minimization of Fouling and Scaling Issues:
Fouling and scaling are common challenges in wastewater treatment processes. Fouling occurs when suspended solids or other contaminants deposit and accumulate on surfaces, such as pipes, membranes, or equipment, leading to reduced efficiency and increased maintenance requirements.
Scaling refers to the precipitation and accumulation of inorganic compounds, such as calcium or magnesium salts, which can hinder process performance. Flocculants assist in minimizing these issues by effectively removing suspended solids and reducing the concentration of scaling-prone compounds. This helps maintain the operational integrity of equipment, prolongs their lifespan, and reduces the frequency of cleaning and maintenance activities.
By harnessing the advantages of flocculants in wastewater treatment, treatment plants can achieve higher treatment efficiency, improved water quality, and reduced environmental impact.
However, it is important to carefully select the appropriate flocculants based on the specific characteristics of the wastewater and the desired treatment outcomes. Dosage optimization and monitoring are also crucial to ensure effective flocculation while minimizing potential side effects.
Types of Flocculants Used in Wastewater Treatment
Flocculants are classified into four major types based on their chemical composition: inorganic, organic, synthetic, and natural. Let’s explore each type in more detail:
1. Inorganic Flocculants:
Inorganic flocculants, such as aluminum sulfate (alum) and ferric chloride, are derived from mineral acids and metal salts. They function by neutralizing the charge of suspended particles, promoting agglomeration and settling. Inorganic flocculants are highly effective at removing suspended solids and phosphorus, making them a popular choice in municipal wastewater treatment plants.
However, their use can lead to the generation of sludge with high metal content, which requires careful handling and disposal.
2. Organic Flocculants:
Organic flocculants are derived from natural substances, such as starch, cellulose, and chitosan. They work by adsorbing onto suspended particles, causing them to agglomerate and settle. Organic flocculants are generally biodegradable and non-toxic, making them an environmentally friendly option.
They are commonly used in the treatment of food and dairy wastewater, as well as in the paper and pulp industry.
3. Synthetic Flocculants:
Synthetic flocculants, such as polyacrylamide (PAM), are made from synthetic polymers. They are highly effective at flocculating suspended particles due to their large molecular size and charge density. Synthetic flocculants are versatile and can be tailored to specific treatment requirements by adjusting their molecular weight and charge characteristics.
They are commonly used in industrial wastewater treatment and in the production of drinking water. However, they can be expensive and may have negative environmental impacts if not properly managed.
4. Natural Flocculants:
Natural flocculants, such as tannins and lignins, are derived from plant extracts. They work by binding to suspended particles, causing them to aggregate and settle. Natural flocculants are biodegradable, non-toxic, and renewable, making them a sustainable option.
They are commonly used in small-scale wastewater treatment systems, such as those found in rural communities and developing countries.
In addition to the four major types, hybrid flocculants can also be used in wastewater treatment. These are combinations of different flocculant types, designed to take advantage of their individual strengths. For example, a hybrid flocculant may combine an inorganic and organic flocculant to achieve enhanced performance and reduced environmental impact.
Let’s just say it…
Why the role of Flocculants in Wastewater Treatment is important in 6 Points?
- Enhanced Water Quality: Flocculants play a crucial role in wastewater treatment by improving water quality. They help remove suspended solids, pollutants, pathogens, and other harmful substances, leading to cleaner and safer water.
- Solid-Liquid Separation: Flocculants aid in the separation of solid and liquid components in wastewater. By promoting the aggregation and settling of suspended particles, flocculants enable more efficient removal of contaminants from the water.
- Efficient Contaminant Removal: Wastewater is a complex mixture containing various contaminants, and flocculants facilitate the removal of these contaminants. By causing suspended particles to form larger clusters (flocs), flocculants make it easier to separate and eliminate contaminants from the water.
- Compliance with Water Quality Standards: The use of flocculants helps wastewater treatment plants achieve desired water quality standards. By reducing the concentration of contaminants, flocculants contribute to meeting regulatory requirements and ensuring the water is safe for various uses.
- Versatile Applications: Different types of flocculants, including inorganic, organic, synthetic, and natural options, offer versatility in wastewater treatment. Each type has its own unique characteristics and applications, allowing for tailored approaches to different wastewater conditions and treatment processes.
- Environmental Impact Reduction: Efficient solid-liquid separation and contaminant removal achieved through the use of flocculants lead to a reduced environmental impact. By effectively treating wastewater, flocculants help protect ecosystems and prevent the contamination of natural water sources.